Hello and welcome to another deep dive. I hope you enjoyed our last deep dive on Franshares.
Today we’ve got another unique, interesting company for you. We’re drilling into a startup called Diamond Standard.
The team at Diamond Standard has raised $45m to create the world’s first regulator-approved Diamond Commodity.
We’ll go into exactly what this means below. Simply put, they’ve created bars and coins containing precisely measured values of diamonds. In doing so, they’re creating the industry’s first standardization. (Get it?)

They’re market-makers; creating a new tradable commodity from scratch. This has never been done before, and is totally unique. Nothing else like it exists.
We’ve been so impressed that we’ve actually invested in their Diamond Standard Fund through our ALTS 1 Fund.
This issue also includes a terrific podcast with CEO Cormac Kinney.
Let’s go
Table of Contents
Summary
- Investment type: There are two options: A fungible Diamond Commodity, and a Diamond Fund
- Accreditation: NOT required for investing in Diamond Commodities. Accreditation IS required to invest in the Diamond Fund
- Minimum investment: $5,000
- Geos: No geographic restrictions for investing. However, only those in the US may physically receive diamond commodities.
- Time horizon: 3+ years. There is also a secondary market for short-term liquidity.
- Website link: Diamond Standard
The diamond market
I’ll be honest here: Outside of jewelry, I didn’t know much about the commercial applications of diamonds.
Turns out, diamonds are incredibly important in multiple industries. Any sector that needs heavy-duty cutting — think mining drill bits, saws, granite — likely uses diamonds. They also make great polishing abrasives and heat sinks.

But heavy industry mostly uses synthetic diamonds. Jewelry is the main driver of natural diamonds.
In 2000, the average price of a diamond was around $15,000 per carat. Fast-forward to 2016, and it doubled to $31,000.
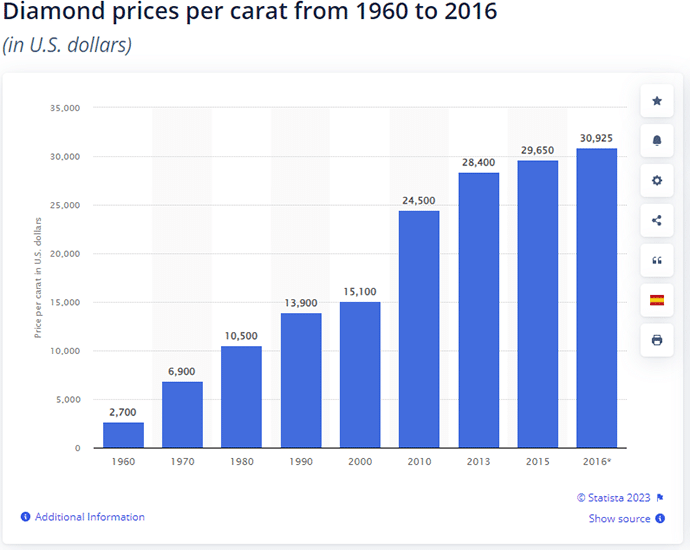
Diamond Standard created an index called DIAMINDX which tracks the price of diamonds. (It will soon be available on Bloomberg)
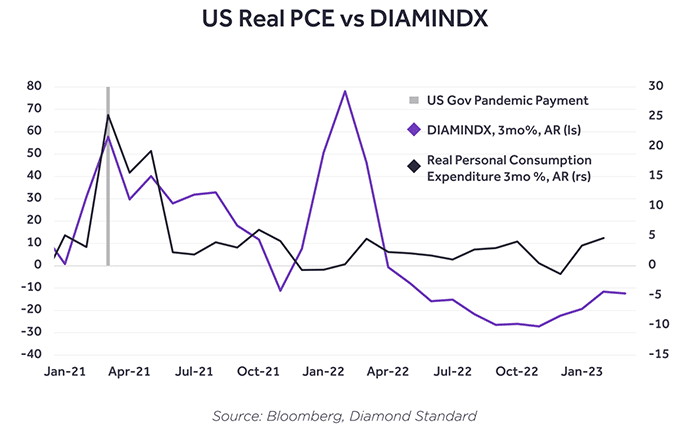
Like many commodities including gold, the index fell in 2022, dropping –8.5%. Today, diamonds are near their all-time lows.
What we see happening here is rather interesting: Demand for diamonds has grown, but prices have fallen. This divergence won’t continue forever.
In fact, the downturn may be already ending, as a massive economic powerhouse that’s been sitting on the sidelines for years is about to re-enter the game: China.
China is the world’s second-largest consumer of diamonds. They’ve finally lifted covid restrictions and Q1 retail sales are up 14.2%.
And diamond prices are already up 17% since the start of 2023.
Diamonds aren’t yet “standardized”
Unfortunately, all this market analysis of diamonds is a bit pointless without standardization.
See, diamonds aren’t like gold, which is easily melted and softly shaped into standard bars weighing exactly 12.4 kg. Each stone is unique. Diamonds vary like crazy in carat, color, clarity and cut, making pricing in a secondary market difficult.
Sure, you can buy diamonds from a jeweler. And some platforms even find and store investment-grade diamonds on your behalf.
But none of this solves the problem of standardization. The lack of standardization prevents fair, liquid secondary markets from forming (and hinders the creation of diamond indices.)
All of this is changing with Diamond Standard’s entry into the market.
What is Diamond Standard?
Diamond Standard offers the only regulated, fungible diamond commodity in the market.
The fact is, Diamond trading and “investing” doesn’t really exist today — at least not in any real sense.
- The retail market is dominated by jewelry and auction houses.
- Unlike gold, diamonds aren’t commoditized.
- There’s no liquidity. Buyers have no real way of selling.
- There’s no way to track investments, or “mark-to-market“
- There are no diamond ETFs.
- There’s no price transparency.
- Nobody knows what diamonds are truly “worth.”
Diamond Standard is trying to change all that, by establishing the equivalent of gold bars for diamonds.
By standardizing diamond investing, they aim to transform diamonds from an inaccessible trillion dollar natural resource into an investable physical and digital asset.
How does Diamond Standard work?
Diamond Standard (with the help of Bloomberg) has created a “permanent statistical index of diamond characteristics.” Think the gold standard, or the gemstone equivalent of the S&P 500.
Here’s how it works:
- Acquire diamonds. The team places transparent bids on natural diamonds from all over the world — ten thousand diamonds at a time. (Indian exporters Hari Krishna are one of their biggest suppliers.) This massive bulk buying forces price discovery, creates a market-clearing price, and allows them to buy a statistical sample of all diamonds.
- Install NFC chips. Each diamond commodity comes with a military-grade NFC chip installed. This has become common practice in high-value supply chain circles, as it ensures simple authentication and quality assurance.
- Assembly. The diamonds are not fashioned into shapes, but rather, attached to coin/bar-shaped frames. Diamond coins and bars are created with an equal value of diamonds in each one; correcting for cut, color, clarity, and carat (weight). Each one is tagged and assembled by the IGI Gem Lab in NYC.
- Storage. These assets are stored in Brinks vaults where they can be delivered to their owners at any time.
- Tie to blockchain. Diamond Standard uses Hedera Hashgraph (after migrating from Ethereum). This unique blockchain technology supports minting a unique digital token to represent the ownership of a diamond. These tokens can be instantly transacted on Diamond Standard’s secondary market for high levels of liquidity.
- Put to market. Finally, Diamond Standard offers investors two standardized commodities to choose from; the coin and bar, a secondary Spot Market to trade them, and an all-encompassing diamond fund.
The amount and value of diamonds is the exact same in every bar. And because they’re the same, they can trade on a market or exchange.
This is how diamonds finally get commoditized.

The Diamond Standard team
Diamond Standard was founded five years ago by Cormac Kinney.
Cormac graduated from Carnegie Mellon with a CompSci background and quickly became a serial entrepreneur.
The man has launched and sold several successful companies, and even has a Wikipedia page with 55 citations. He’s the real deal.
- He’s the guy behind heat maps. In 1993, he co-founded NeoVision to develop heat maps. This revolutionary software sorted financial market information into a 2D color scheme. Although the concept had been around for ages, Kinney was the first to trademark the term. “Heat maps” have now been used in over 200,000 research papers.
- He sold a media software company to Rupert Murdoch. Kinney created a new social network in 2013, simply called “Network.” (Side note: Does he has a penchant for great names or what?) It was a business-focused media system intended to track the articles consumed by professionals in a certain industry. It would then use these habits to develop a taste profile for individuals. The tech was acquired by Rupert Murdoch’s News Corp and applied to The Wall Street Journal in 2015.
Horacio had the pleasure of sitting down with Cormac for a 38-minute interview. I highly recommend you watch or listen to this one, it’s really interesting:
What’s next for Diamond Standard?
Wirehouses
Diamond Standard recently announced a partnership with GBI. As an alternative asset manager, GBI is distributing Diamond Standard’s diamond commodity to Goldman Sachs, UBS, Fidelity, Stonex and so on.
This gives Cormac Kinney and his team exposure to some of the industry’s biggest wirehouses (i.e., brokers and securities dealers). It means that RIAs and wealth managers can finally use Diamond Standard to invest in diamonds for their clients.
Diamond ETF
Next up is perhaps Diamond Standard’s biggest play yet – they want to create a diamond-themed ETF.
Diamond Standard is regulated by the Bermuda Monetary Authority (the company is HQ’d in the US, but their diamond commodities are regulated by Bermuda), and has already had one fund approved by the SEC. It’s likely they will eventually be successful here.
Diamond derivatives
Diamond Standard is also waiting for SEC and CTFC approval on derivatives — specifically, diamond futures and options.
Once available, these will be traded on the CME Globex Exchange to give experienced investors a way to trade.

Investment opportunity
Diamond Standard offers three investment products, each suiting a different type of investor.
Diamond coins
The cheapest option is diamond coins. Their unit price is updated weekly, but at the moment it’s sitting at just under $5k ($4,940).
Each diamond coin gives investors access to BCC – a digital token running on Hedera that can be used to trade on Diamond Standard’s Secondary Spot Market.
Diamond bars
Next up are diamond bars. These are similar to coins, but worth 10x the coin’s market value (currently $49,400).
Diamond Standard Bars come with the unique BCB digital token, which allows remote transactions of diamonds on the secondary marketplace.
Although the diamond bars and coins might not look exactly the same, they will always add up to equal the same carat, weight, color and clarity.
Diamond investment fund
Finally, Diamond Standard offers a private investment fund with a $100,000 minimum.
The Diamond Standard Fund is an investment vehicle in partnership with asset manager Horizon Kinetics. The fund gives eligible investors exposure to diamonds without having to worry about actually owning them (like with the bars and coins).
The fund’s NAV is based on Diamond Standard’s DIAMINDX index, updated every Friday.
Liquidity
Both of Diamond Standard’s commodity offerings — Coin and Bar — are linked to a digital token hosted on the Hedera Hashgraph blockchain. This makes it easy for investors to buy, sell and swap their diamonds.
To date, the total transactions on the P2P Diamond Standard Spot Market amount to $2.5m. The average trade value is close to $10k from 730+ participants.
It’s not a massive market yet, and it might take up to seven days for your order to execute. However, it’s the closest diamond assets have ever been to liquid, and will likely improve over time.
A few caveats:
- To trade your diamonds on the secondary market, your asset must be stored in the Brinks vault.
- If you want to trade a diamond that’s been sent to your address, you must send it back to Diamond Standard – at your own expense.
- Only once the diamond is secured in Diamond Standard’s custody will the investor’s BCC/BCB tokens be activated for trading on the Spot Market.
- Spot Market prices are all quoted and settled in USDC. So investors need an ERC-20 wallet to participate.
- The Diamond Standard Fund is a bit less liquid. Each investor must hold their shares of the fund for 12 months before they become eligible for resale.
Fees
The Diamond Standard Fund has a standard management fee of 2%.
The Diamond Standard bar and coins charge a 3.5% exchange fee. For one unit of the company’s cheapest offering, this would equate to $172 in fees.
There are no performance fees.
Who can invest in Diamond Standard?
Anybody can invest in the Diamond Standard commodities (coins and bars). The current price for a coin is just under $5,000, so it’s pretty accessible.
The Diamond Standard Fund is restricted to accredited investors only.
For now, delivery of diamonds is only available to USA customers. However international investors can still sign up and purchase a representative ownership token to participate in secondary markets.
Regulation
Diamond Standard undertakes regular audits from Deloitte to ensure their accounting is up-to-date and transparent. The business is currently regulated by the Bermuda Monetary Authority, making it the only regulated diamond commodity offering in the world.
Each Diamond is inspected and cleared by international and national gemstone inspection agencies (IGI and GIA|).
Additionally, the CFTC has approved Diamond Standard commodity coins and bars as “good for delivery” for listed futures and options.
Derivatives will likely go live in 2023.
How does Diamond Standard stack up?
Returns potential
Like gold, but with stronger upside
Diamonds have underperformed the S&P 500 by 17% since 2020.
But charts don’t tell the full story. There are a few important things going on with this market:
- China is re-entering the market after years on the sidelines
- Prices are near all-time lows, and in 2023 it’s already up
- Supply of new diamonds have been falling, while demand is rising. There haven’t been any new diamond mines discovered in 20 years. Supply is falling by 2-4% per year. As the known global diamond reserves continue to be mined and depleted while the global demand for diamonds increases, a diamond demand-supply gap is expected to develop in the coming years. By 2050, there is a forecasted supply shortfall of some 278 million carats of diamonds worldwide.
- And biggest of all, this $1.2 trillion dollar market has been basically inaccessible to investors until now. There’s a good chance Diamond Standard themselves will actually create new demand.
Competition
The only regulator-approved diamond commodity
There are a couple of asset managers around who offer investment vehicles for diamonds. But Diamond Standard is the only regulated company with a commodity on offer.
They are making a new market before our very eyes.
History
A bit concerning
The problem isn’t competition, it’s the history of what they’re attempting. The landscape is littered with companies who have tried something similar before, and failed.
- Specialized diamond fund Diamond Circle Capital listed in London in 2008 before liquidating its gemstone portfolio five years later.
- IndexIQ filed a prospectus to set up a diamond ETF in 2012 but never launched.
- And Swatch-owned jeweler Harry Winston had plans the same year to set up a $250mn fund to buy diamonds with money from institutional investors. It didn’t work out.
Traction
Gaining traction
Since 2018, Diamond Standard has raised $45m in private capital and remain debt-free. 4,000+ investors have used their platform so far.
They’ve got media coverage on Bloomberg and FOX.
According to the company’s projections, their revenue is set to inflect substantially in H2 2023 — with an anticipated nine-figure annual run rate.
Leadership
Fantastic
Cormac Kinney is a big deal. He’s built and exited multiple successful businesses in a range of industries.
Kinney is supported by Head of Capital Markets Greg Giannakopoulos, President Doug Jordan and asset manager Mark Lieberman.
The leadership here is top-notch.
Fees
Reasonable (and no performance fee)
3.5% as an exchange fee is a bit on the expensive side, but makes sense considering all the legwork Diamond Standard has to do to procure the physical and digital elements of their product.
The Fund’s fee of 2% is normal, and the lack of a performance fee is appealing.
Closing thoughts
Diamonds are the hardest gemstones in the world. But Diamond Standard has figured out a way to make them liquid.
For decades, gold, silver, platinum and palladium have dominated the precious metal commodity markets. Diamonds weren’t invited to the party, because they’re so notoriously illiquid and tough to standardize.
This is all about to change thanks to Diamond Standard.
An all-new asset class is opening up, and Diamond Standard is the market-maker bringing it all to life. It’s pretty incredible. Their coins and bars are the first-ever regulated fungible diamond commodities. And a diamond ETF and derivatives are next.
There’s no guarantee that diamonds will take off in the way gold has. The diamond industry can only dream of replicating even a slice of the gold industry’s success.
But when State Street launched the first gold ETF in 2002 (SPDR), the price of gold grew by 47% per year. And the accumulation by investors is what drove the price up. The same thing happened with Uranium.
Despite rising demand and reducing supply, diamond prices are near their all-time lows today. And if Diamond Standard succeeds in bringing the ETF to life, diamond prices could rise 300-500% — just like they did with gold.
Could this really happen?
We think so, which is why we invested in Diamond Standard.
It’s worth considering.
Disclosures
- Diamond Standard is an Alts sponsor, and this was a paid deep dive.
- We have made an investment in the Diamond Standard Fund through ALTS 1.
- This issue contains affiliate links to Diamond Standard.
This issue is a sponsored deep dive, meaning Alts has been paid to write an independent analysis of Diamond Standard. Diamond Standard has agreed to offer an unconstrained look at its business & operations. Diamond Standard is also a sponsor of Alts, but our research is neutral and unbiased. This should not be considered financial, legal, tax, or investment advice, but rather an independent analysis to help readers make their own investment decisions. All opinions expressed here are ours, and ours alone. We hope you find it informative and fair.