Why the pendulum swings back & forth
The modern streaming market isn’t just crowded, it’s completely overrun with options.
In this issue, we explore the media bundling pendulum swing. How it works, where we are in the cycle, and and why re-bundling is an inevitability.
Media is an industry we know well, and this topic hits close to home.
Let’s go 👇
Table of Contents
Invest in the future of news bundling
The problem is simple: Paywalls are everywhere, but paying for access to every news site is unrealistic.
A new startup called Zette lets people legally access paywalled articles with a single subscription.
They’re raising on Wefunder, and Alts readers have an early opportunity to invest.
The bundling wave that has swept over music, movies, and TV has somehow skipped news media.
But with a billion paywalls getting hit each day, the industry desperately needs a solution like this.
They already have 50,000+ readers, and partnerships with The Miami Herald, The Sacramento Bee, and Forbes.
You can invest in Zette’s friends and family round.
Invest in the future of news bundling →
The economics of media bundling
In 2007, Netflix fired the opening shot in the war on cable, introducing video streaming with over 1,000 titles.
The streaming model was (and remains) very threatening to traditional TV. Instead of paying $100/month for pre-programmed shows chock full of ads, viewers could pay $10-20 a month for on-demand viewing with no ads.
The idea proved immediately popular, with Netflix registering more than 20 million subscribers in just three years.
Other streamers popped up on the back of that success, including Hulu Plus and Amazon Prime Video.
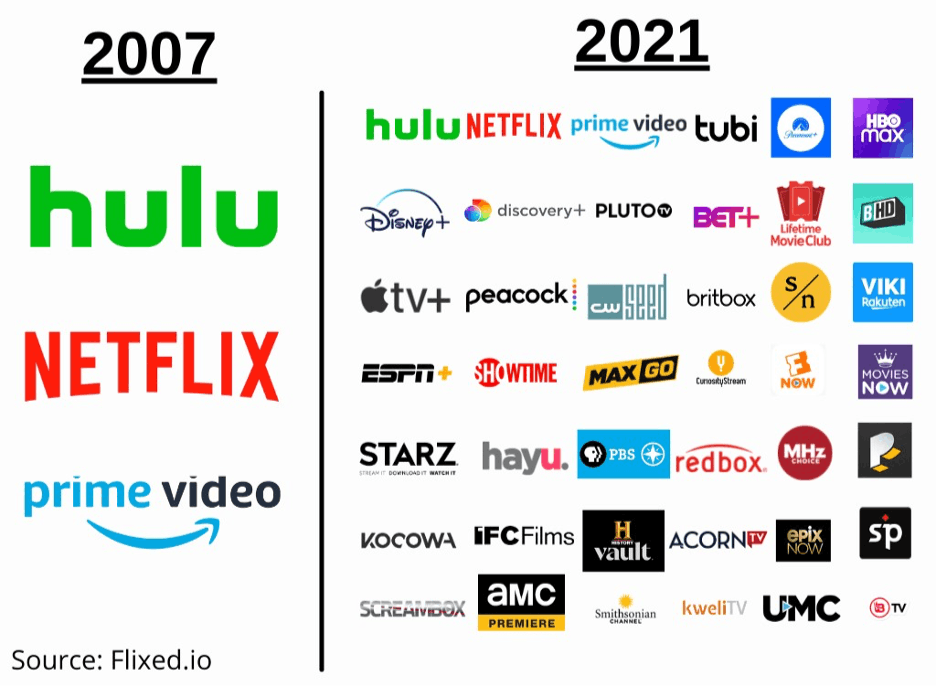
But as streaming prices have risen, and a new streaming company seems to launch every few months, an odd reversal is starting to happen: The new streaming model is beginning to look a lot like old cable TV.
Mergers are becoming inevitable. And bundles, where multiple streaming services are combined into a single subscription, are getting more popular.
It’s easy to laugh at this pendulum swing, seeing it as the hubris of Silicon Valley finally confronting economic reality.
But digging underneath, the rise of bundles creates a bunch of interesting questions:
- Was the original streaming model inherently unsustainable?
- What do bundles look like in other forms of media? (Like music, TV, and news)
- What does all this mean for investing in media?
Today, we’ll discuss why media bundling is an inevitability. We’ll start by exploring the most counterintuitive idea in media economics.
The paradox of bundling
No discussion of bundling would be complete without former Netscape CEO Jim Barksdale’s famous quip:
Gentlemen, there are only two ways I know of to make money: bundling and unbundling.
The quote has become cliche, but it captures a fundamental truth about bundling: aggregating product offerings can create value, but so can doing the opposite.
This is the paradox of bundling, the idea that both bundling and unbundling can both be viable business strategies.
There’s one industry which provides the perfect long-term case study for this concept: Music.
From singles to CDs (and back)
Back in the 90s, CDs were the dominant distribution format for music, sold at retail stores like Tower Records.
(Side note: Don’t sleep on CDs as an alternative investment!)
CDs are basically a form of bundling. Instead of buying a single, 15 songs sold on the same disc.
(The true original music bundles were 12″ LP records. LP stands for “Long Play”, as opposed to the 7″ singles that were originally popular.)
But here’s the thing — songs on an album aren’t all equally valuable. And most people bought CDs for just a few tracks.

So, when Apple introduced the iTunes Store in 2003, the stage was set for singles to become the dominant distribution format.
Everyone thinks the success of iTunes was a technology story. And it was!
But more importantly, iTunes was a story about the unbundling of CDs.
By 2012, singles outsold CDs 7 to 1, and Tower Records closed (although they’ve since reemerged as an online shop for nostalgia-driven music fans).
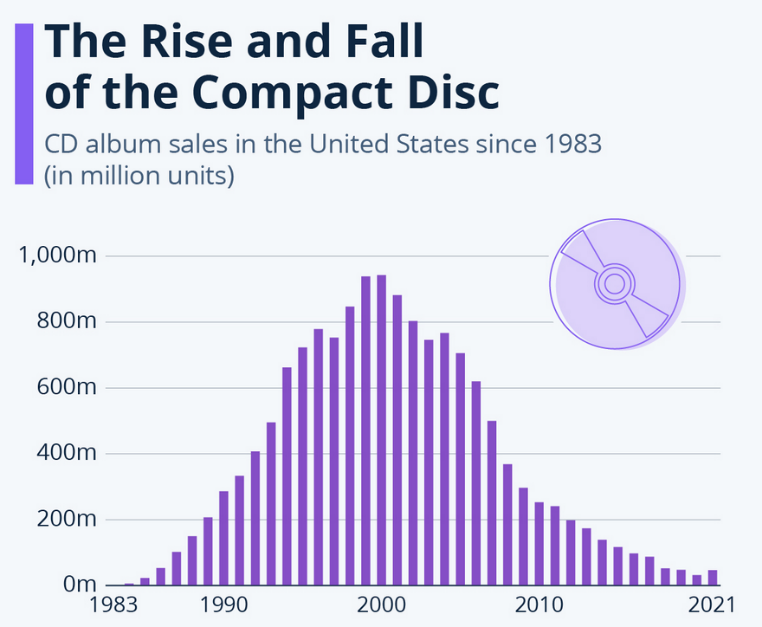
As we know, iTunes downloads would eventually give way to the rise of music streaming services like Spotify. In 2015, Apple would even introduce its own streaming service.
Music streaming represents a rebundling. Instead of selling individual songs, it gives subscribers access to the world’s largest CD for a fixed monthly price.

The bundling and unbundling cycle
Phase 1: Bundling pleases everyone
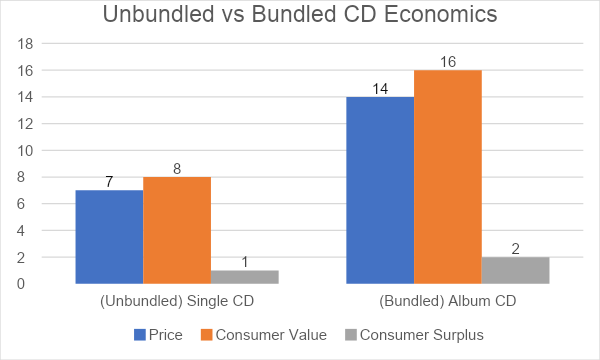
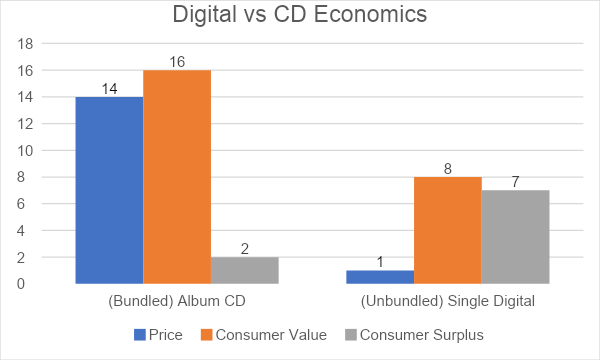
Let’s say that a music fan values a hit song at $8, and the remaining 14 songs on the same album at another $8 altogether.
A CD distributor may be able to sell the fan a disc with the single hit track profitably for $7, providing $1 in value (what’s known as consumer surplus).
But placing a few extra tracks on a CD isn’t very expensive. So the distributor could put 15 songs on the album on it and sell it for $14.
Higher profits for the distributor, and better value for the fan ($2 as opposed to $1). Win-win.
This is the core logic of how bundling benefits both companies and customers: selling “add-ons” that the customers probably wouldn’t pay for individually.
Phase 2: Bloat leads to unbundling
But here’s what happens next: Bigger bundles create bloat.
After all, it’s not a foregone conclusion that a 20-song album is more valuable than a 10-song album. What if all the extra tracks just make it hard to find the really good ones?
Offering bundles instead of à la carte options (i.e. singles) can cause customer resentment. “Why do I have to pay for all this extra stuff? Now there’s more crap to sift through!” etc.
Technological innovation accelerates the unbundling process even further.
Take newspapers, for example. No industry has seen how much tech can disrupt a sector like newspapers have.
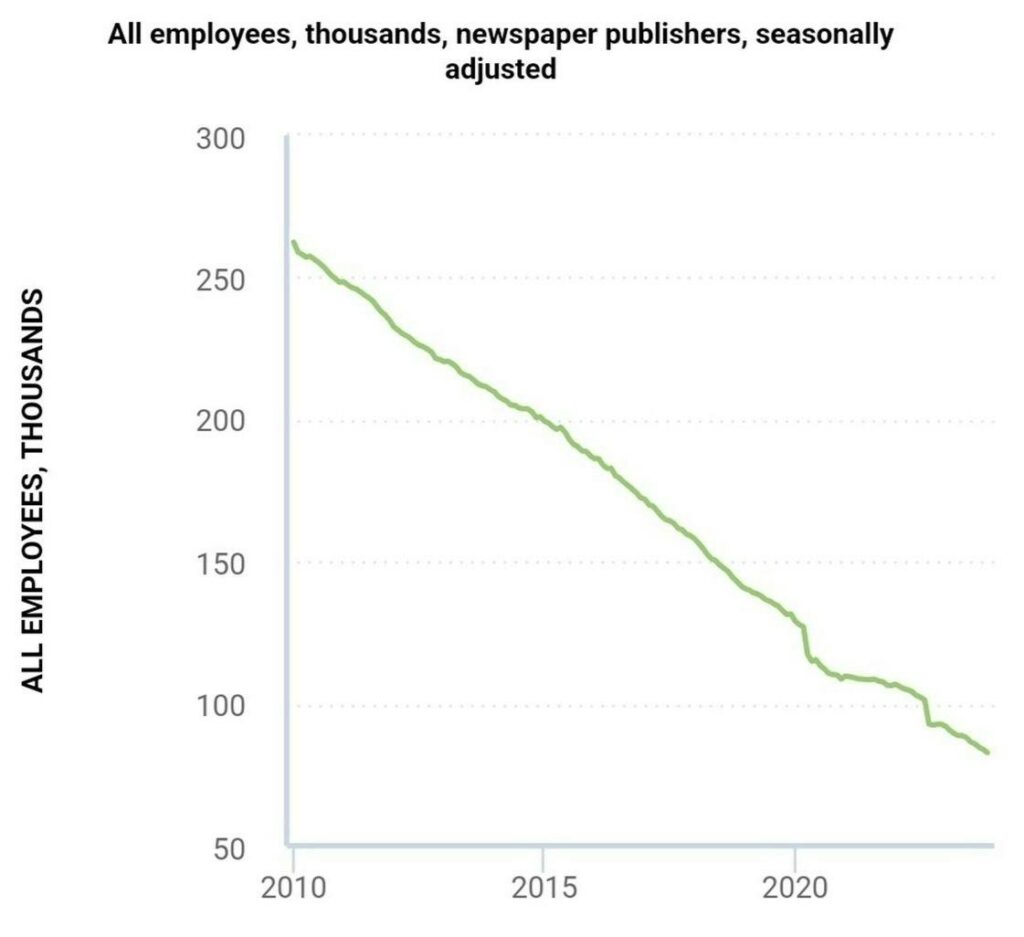
Back to music. When the internet cut the cost of distributing music to almost nothing, platforms like iTunes were able to offer hit songs for just 99¢.
This alone provided far more customer value than the $14 CD, even though the extra songs weren’t included.
It goes like this:
- Customers flock to the higher-value offering
- Bundlers start to fall apart (like say, Tower Records, or cable companies)
- Unbundlers rapidly gain market share
Phase 3: Unbundlers must re-bundle to grow
While not offering singles causes resentment, offering too many singles creates frustration as well.
“Why do I have to purchase one song at a time? Can’t I just pay one price for everything?”, etc. It’s basically the inverse of bloat, and it further motivates bundling.
But the bigger problem is growth. Once the industry has splintered into a mess of unbundled offerings, the unbundlers run into a growth wall.
There’s a natural roadblock here: only so many people are willing to pay 99¢ for individual songs. Once you’ve exhausted the sale of rock songs to rock fans, rap songs to rap fans, etc., growth becomes challenging.
Can you sell a rap song to a rock fan? They probably won’t pay full price, but they’d be interested if it was a cheap add-on.
Ultimately, this logic ends with music streaming services like Spotify, — the biggest music bundle possible.

Now let’s turn to the TV streaming industry; where the swing back to bundling is causing a bit of an identity crisis.
Why streaming is (slowly) becoming cable TV
When it started, companies like Netflix unbundled movies and TV shows from cable TV.
TV unbundling has similar motivations to those of the music industry — frustration with TV channel bloat and the superior economics of internet distribution.
But now, Phase 3 is well underway. Unbundlers need to pursue profitable growth in an increasingly saturated market, leading to a streaming universe that’s looking more and more like cable.
Organic, unbundled growth slowed
As the original streaming service, Netflix also provides the most instructive example of how the industry is changing.
After strong pandemic-related growth, Netflix experienced its first quarterly decline in subscribers in 2022. This led to a 35% one-day drop in its stock price.
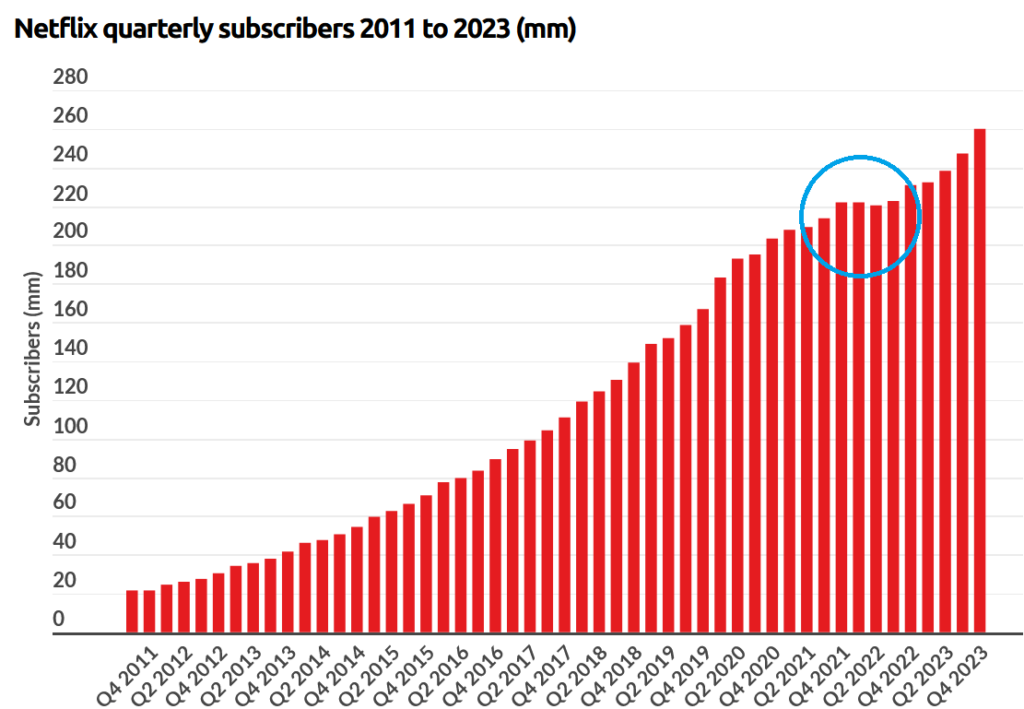
If the subscriber count were to drop, it really shouldn’t be too surprising. After all, Netflix competes not just with cable, but with all entertainment. There are only so many people with the desire to pay for Netflix.
But for Netflix that would be an unacceptable conclusion – not just because investors demand continuous growth, but also because of the need to justify the enormous sums of money the company has spent on content.
Netflix spends about $17 billion per year to produce new shows and movies. About half of the company’s revenue goes towards content.
Subscription fatigue
And the subscription model has contributed to subscription fatigue – the friction associated with managing so many different logins and payments.
This is a stark contrast from the peak content wars of the 2019-2022 period, when streamers seemed happy to burn money on new shows and movies with no concern for immediate profits.
This new focus on the bottom line isn’t limited to the TV streaming industry — it’s something being seen all over the media landscape.
Media’s massive consolidation phase
Streaming is a subset of media, and large cap media is doing poorly right now:
- The ad market (which generates a ton of media revenue) had tepid growth in 2023, and there’s tremendous uncertainty about what 2024 will bring.
- Everyone’s feeling it. Both traditional and digital publications have struggled, with revenue at Vox down 15% and The Washington Post cutting 10% of its workforce.
- Meanwhile, following the writers’ strike and poor results for both traditional TV and streaming, Warner Bros, Disney, and Paramount all had layoffs in the past year.
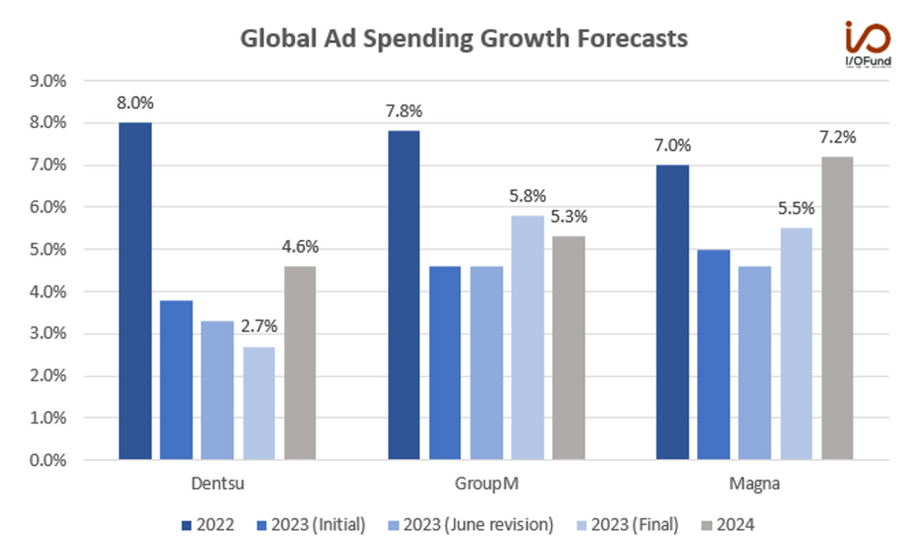
And this isn’t just about the ad market. The internet as a whole has dramatically lowered the cost of distributing media (something we saw with both streaming and music).
With an influx of new competitors, it’s harder for individual outlets to command the attention needed to generate revenue. Mergers are inevitable.
Social media hasn’t helped either. The global average for social media use now clocks in at 2.5 hours per day.
Ads are coming back
Netflix and Amazon Prime Video both started out offering ad-free viewing as a key part of their subscription models.
But both platforms have introduced ads in response to slowing subscriber growth and the need to attract a broader audience by offering a cheaper option.
The ad-supported tier is priced lower, but viewers are upset how they occur randomly, instead of in naturally occurring ad breaks.
The simiple fact is this: Media companies can no longer rely on just subscriptions or ads — they need to do both.
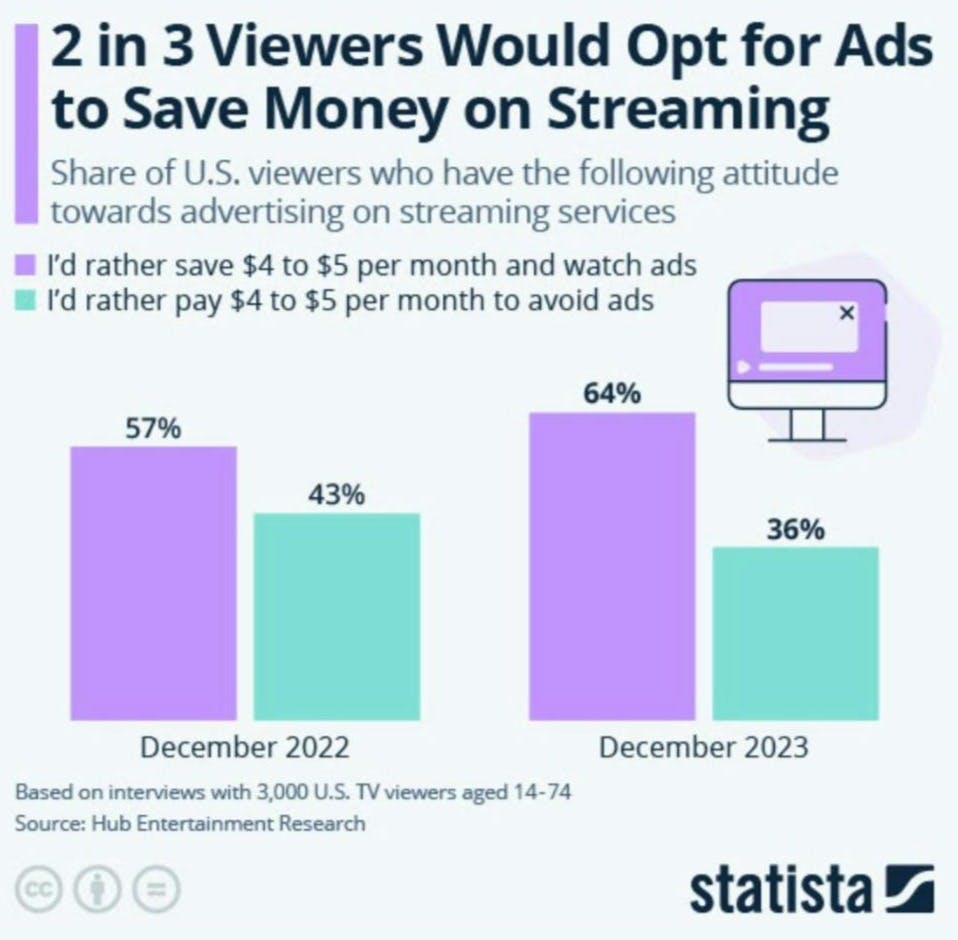
And surprisingly, consumers have shown that they don’t really care. In a recent study, 64% stated they would watch ads if it meant they could save money.
As The Verge puts it: Netflix is different now, and there’s no going back.
Paywalls are spreading like crazy
As a result, media outlets are searching for new avenues for profit. Paywalls have proved a popular option.
From 2017 to 2019, the portion of US newspapers with a paywall jumped from 60% to 76%.
And survey figures show that the importance of paywalls has climbed, with 80% of media companies now indicating that paywalls or subscriptions are a very important revenue stream — up from 74% in 2020.
As a media company, Alts isn’t immune from these trends! You may have noticed some of our best content is now behind a paywall (But ironically, not this issue! So meta.)
But traditional media companies have so far failed to pursue bundling. And it’s a bit surprising, because (as we saw in both streaming and music) bundling is a powerful way to increase revenue by selling to customers who wouldn’t otherwise pay.
How investors can profit from these trends
Interestingly, the bundling wave that has swept over music, TV and movies, has somehow avoided news media.
But there is one company we discovered that is both riding the wave of increased paywalls and accelerating bundling as a media strategy.
Zette offers a much-needed concept: you can unlock paywalled articles from over 100 publishers with a single subscription.
Zette is growing into what music streaming bundles have become and what video streaming bundles are trying to be — one payment that unlocks an entire industry.
They’re also ahead of the game in AI, building out a feed that can offer a personalized (and fact-checked) summary of news.

But perhaps the more exciting opportunity for you isn’t Zette as a service, but as an investment.
The company is in early bird funding on Wefunder, meaning investors get access to a valuation that will increase after the first $300k is raised.
On the supply side, news media is realizing they need to bundle to grow. I’d expect their publisher count to increase. (Heck, we’d love to join their platform ourselves!)
On the demand side, consumers are realizing that paywalls aren’t going anywhere. I think Zette’s value prop is strong. They’ve already signed up more than 50,000 registered readers, and I’d expect strong reader growth this year.
I think this idea could work, and I hope it does. Especially because this is an election year, and access to high-quality journalism is more important than ever.
See you next time,
Brian
Further reading
- Stratechery was one of the first to identify the bundling/unbundling pendulum swing
- Chris Dixon talks about how bundling benefits buyers and sellers
- The Four Myths of bundling
- Satellite radio never unbundled, but SiriusXM is using a “human curated” focus to take on music streaming rivals
Disclosures
- This issue was sponsored by Zette
- Neither the author nor the ALTS 1 Fund has any holdings in any companies mentioned in this issue
- This issue contains no affiliate links